10 Best Statistical Mapping Software for Demographic Analysis to Unlock Insights
In today’s data-driven world, understanding demographics is crucial for making informed decisions. The right statistical mapping software can transform complex data into insightful visualizations, helping you uncover trends and patterns. Whether you’re a researcher, marketer, or urban planner, choosing the best tools can elevate your analysis and drive impactful results.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases. Thank you!
ArcGIS
ArcGIS, developed by Esri, is a premier platform for mapping and analyzing demographic data. It’s known for its comprehensive integration of various data sources. With access to Esri Demographics, U.S. Census Bureau datasets, and American Community Survey (ACS) data, you can conduct extensive analyses effortlessly. ArcGIS offers features like ready-to-use layers and web maps through the ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World, enabling detailed demographic reports, economic assessments, and insights on at-risk populations. Tools like ArcGIS Business Analyst further enhance your user experience, helping you identify market trends and create compelling infographics.
Explore world history with this comprehensive atlas! Featuring detailed maps and timelines, this book provides a clear and engaging overview of key events and civilizations across the globe.
QGIS
You’re often faced with the challenge of visualizing complex data in a clear and informative way. Effective mapping requires not just the right tools but a solid understanding of how to leverage those tools for the best results.
Technical Context
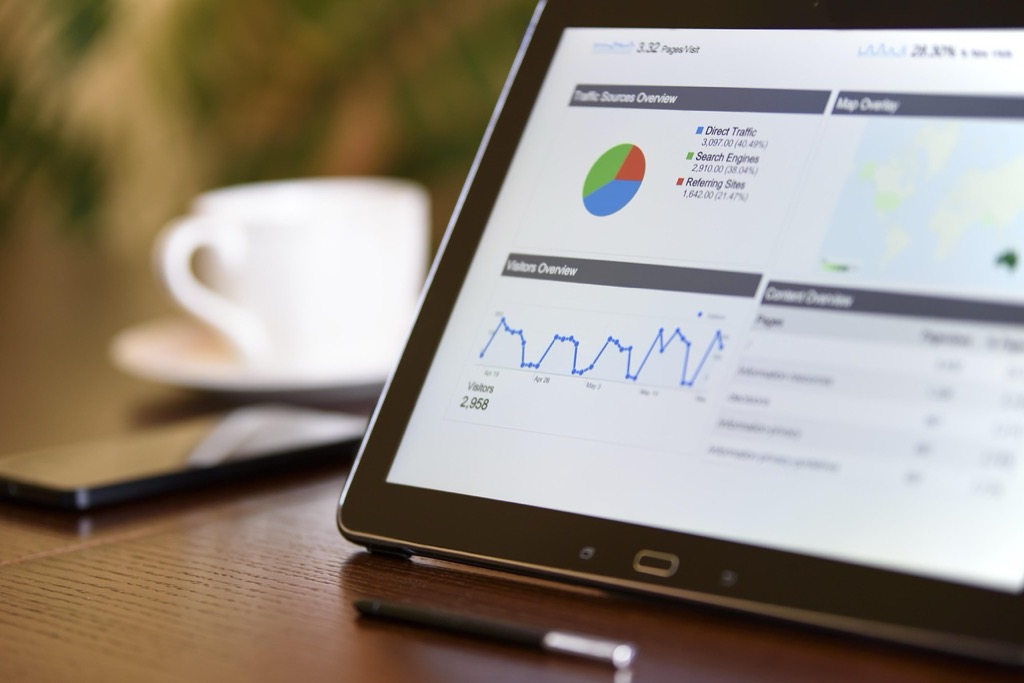
In today’s mapping landscape, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are pivotal. They allow you to analyze, visualize, and interpret spatial data. By harnessing GIS, you can convert raw data into compelling maps that reveal trends, relationships, and insights about demographics.
Key Methods with Examples
- Layering Data: Use vector and raster layers to separate different data types. Tools like QGIS let you overlay demographic data with geographic features, resulting in a nuanced understanding of population distributions.
- Thematic Mapping: Employ thematic maps to highlight specific characteristics. For instance, heat maps are effective for visualizing areas of high population density, while choropleth maps illustrate variations in demographic attributes across regions.
- Proximity Analysis: Utilize tools like ArcGIS Pro to conduct proximity analysis. This helps to identify resources close to specific populations, such as schools or hospitals, which is especially useful for urban planning.
Common Technical Issues
Be prepared for some common challenges. Data compatibility issues often arise when integrating different datasets. Always ensure your data sources conform to standard formats such as GeoJSON, Shapefiles, or CSV to maintain integration ease. Cleaning your data is essential—remove duplicates and verify accuracy before visualization.
Data Visualization Options
Your visualization choices can significantly impact how data is interpreted. Here are some options to consider:
- Static Maps: Create high-resolution static maps using tools like Adobe Illustrator for presentation-focused work.
- Interactive Maps: Leverage web mapping platforms like Mapbox or Leaflet for engaging stories that allow users to explore data dynamically.
- Dashboards: Build dashboards with Tableau or Microsoft Power BI to combine multiple visualizations in one interactive interface.
Workflow Frameworks
A well-structured workflow can streamline your mapping projects. Start by clearly defining your goals and audience, then gather and clean your data. Next, utilize GIS tools for analysis before creating your visual outputs. Incorporate feedback at every stage, ensuring the final product meets stakeholders’ needs.
Quality Control Tips
Quality assurance is crucial in mapping. Implement the following procedures:
- Data Validation: Double-check all datasets for accuracy and consistency. Cross-reference with reputable sources like the U.S. Census Bureau.
- Peer Review: Get a second pair of eyes on your maps. Feedback can highlight potential oversights.
- Version Control: Use version control systems like Git for GIS projects to track changes and maintain organization.
By addressing these aspects, you’ll enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of your mapping efforts, resulting in impactful visualizations that effectively convey demographic information.
Tableau
You’re navigating a rapidly evolving landscape in digital mapping where complex data sets and user expectations collide. The challenge of creating maps that convey clear information, while integrating various data sources, can be daunting.
Technical Context for Effective Mapping
Understanding the core principles of GIS (Geographic Information Systems) is crucial. Establishing a strong technical foundation helps you leverage mapping software effectively. Popular tools like ArcGIS and QGIS provide robust features for data integration and visualization.
Key Methods for Effective Cartography
- Data Layering: Use layers to manage multiple data sets effectively. For example, overlay demographic data on geographical features to highlight trends.
- Thematic Mapping: Create thematic maps that represent specific data aspects, such as population density or socio-economic indicators.
- Proximity Analysis: Use proximity analysis to understand spatial relationships, helping to identify accessible services in relation to population centers.
Common Technical Issues
You may encounter challenges with data compatibility when importing various formats. Ensure your data is clean and well-structured to avoid integration issues. Additionally, watch for scale discrepancies that can distort your visualizations.
Data Visualization Options
You have several data visualization tools at your disposal:
- Interactive Dashboards: Tools like Tableau allow users to create interactive, user-friendly dashboards for dynamic data representation.
- Static Maps: Use static maps generated from GIS software for reports and presentations where interactivity isn’t critical.
- 3D Mapping: Elevate user engagement with 3D maps that provide a more immersive view of your data.
Workflow Frameworks for Mapping Projects
Establishing an effective workflow is key to project success. Here’s a streamlined process you can follow:
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline the goals of your mapping project.
- Data Collection: Gather and validate data from reliable sources.
- Design and Create: Use GIS software to design your map, applying appropriate visualization techniques.
- Peer Review: Collaborate with colleagues for feedback and validation.
- Version Control: Keep track of changes in your files to maintain accuracy.
Quality Control Tips
Implement rigorous QA/QC procedures to ensure accuracy:
- Conduct data accuracy checks regularly. Validate data against reliable sources to avoid inaccuracies.
- Apply peer reviews for feedback on map clarity and context.
- Document your mapping processes for accountability and future improvements.
By grounding your mapping efforts in these principles and practices, you foster not only clarity and precision in your efforts but also enhance the overall effectiveness of your cartographic outputs.
MapInfo Pro
MapInfo Pro is a powerful Geographic Information System (GIS) software that’s invaluable for demographic analysis. It’s known for its user-friendly interface and robust capabilities in location intelligence, making it a preferred choice for professionals.
Improve disaster response with GIS. This book provides practical guidance on using GIS tools and techniques for effective planning, mitigation, and recovery efforts.
Overview and Strengths
MapInfo Pro combines dynamic demographic data with mobile location data, transforming static datasets into actionable insights. You can visualize how populations shift during different times, revealing critical patterns like daytime versus nighttime demographics. This versatility allows users to perform comprehensive demographic analyses, understand consumer behavior, and make informed spatial decisions efficiently.
Use Cases in Demographic Analysis
You can leverage MapInfo Pro for various demographic analysis applications. For instance, retail businesses can use it to determine optimal store locations based on population movements. Urban planners can analyze shifting demographics when designing public services. Additionally, marketing analysts can visualize target markets to tailor their strategies effectively. Each use case demonstrates MapInfo Pro’s capabilities in supporting precise, data-driven decision-making.
Mapping effectively can be a challenge, especially when it comes to visualizing complex datasets. As a cartographer, you often face hurdles in conveying meaningful insights through your maps while ensuring accuracy and clarity.
R with ggplot2 and Leaflet
Understanding how to integrate various mapping tools with Geographical Information Systems (GIS) is crucial. Powerful software such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and R packages like ggplot2 and Leaflet offer features that enhance data visualization capabilities. Incorporating these tools helps you leverage demographic data effectively.
Key Methods for Effective Mapping
- Data Layering: Combine multiple datasets, such as population density and income levels, on one map to enhance analysis. This allows you to identify correlations across demographics.
- Thematic Mapping: Use color gradients or symbols to represent trends, such as income disparity or educational resources. For example, a population pyramids with
ggplot2can provide insight into age distribution. - Proximity Analysis: Determine the distance between important locations in your study area—such as schools and population centers—to assess accessibility.
Common Technical Issues
When mapping, data compatibility can present challenges. Here are several issues you might encounter:
- Data Format Mismatches: Ensure your datasets are in compatible formats, such as shapefiles for GIS applications or CSV files for statistical software.
- Scale Discrepancies: Be aware of varying geographic scales in your data. Use normalization techniques to maintain consistency.
Data Visualization Options
Several visualization methods can enrich your mapping presentations:
- Static Maps: Good for reports or print media, they present clear, concise data visualizations.
- Interactive Maps: Leverage libraries like
Leafletto create engaging, user-friendly maps that allow for deeper exploration of your data. - Dashboards: Combine maps, charts, and tables into one cohesive presentation to provide multiple data perspectives at once.
Comparison of Best Statistical Mapping Software for Demographic Analysis
Navigating the landscape of statistical mapping software requires an understanding of various factors like pricing, ease of use, and performance. By evaluating these aspects, you can choose the tool that best meets your demographic analysis needs.
Pricing and Licensing
Pricing structures vary among mapping software. Some tools, like ArcGIS, operate on subscription models, which might add up over time. Conversely, Maptitude offers a one-time purchase without ongoing fees. The value of included demographic data can offset initial costs, making it efficient for budget-conscious users. Always consider how licensing affects accessibility to updates and support in your evaluation.
Explore the world with Maptitude, a geography-based board game. Test your knowledge of countries, capitals, and continents in a fun, competitive way.
Ease of Use
User-friendliness is essential for effective demographic analysis. Tools like Tableau and Maptitude stand out for their intuitive interfaces and wizard-driven tools. These features simplify complex tasks such as layering maps and analyzing Census data. If you prioritize speed in learning a new software, opting for platforms with pre-designed templates can significantly reduce the time spent on setup and execution.
Performance and Speed
When evaluating performance, speed is crucial, especially for large datasets. QGIS often excels in handling extensive data thanks to its robust architecture, enabling quick rendering of complex maps. In contrast, ArcGIS offers high-performance capabilities through efficient data processing, but may require more system resources. Ensure that your hardware can support the software you choose, as performance can vary based on data size and complexity.
Conclusion
Choosing the right statistical mapping software is crucial for effective demographic analysis. With the right tools at your disposal you can transform complex data into clear visualizations that reveal valuable insights. Whether you opt for ArcGIS, QGIS, Tableau, or Maptitude each offers unique features that cater to different needs and expertise levels.
As you navigate your options keep in mind the importance of user-friendliness data integration capabilities and visualization tools. By applying best practices in data preparation and visualization you’ll enhance your ability to make informed decisions based on demographic trends. Embrace these tools and techniques to elevate your mapping skills and achieve impactful results in your analysis.