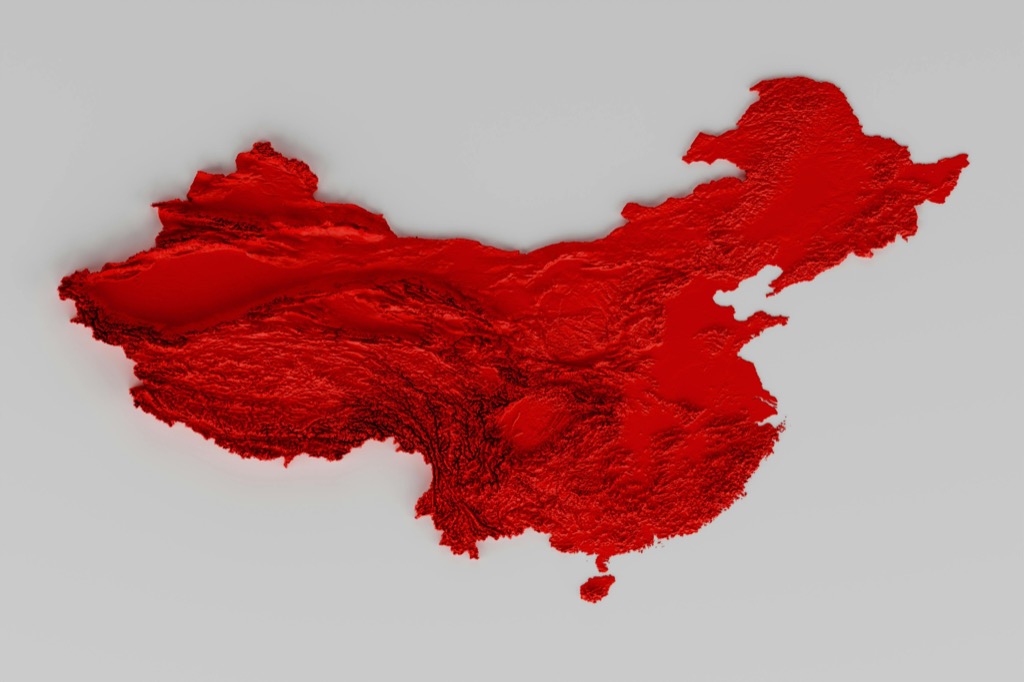
10 Best Software for 3D Map Modeling That Transform Digital Maps
In today’s digital landscape, creating stunning 3D maps has never been more crucial for industries like urban planning, gaming, and environmental science. The right software can transform your ideas into detailed, interactive visualizations, making complex data more accessible and engaging. This guide explores the best software options available, helping you choose the perfect tool for your 3D mapping needs.
ArcGIS Pro
ArcGIS Pro is a powerful tool that integrates advanced visualization and analysis capabilities. Its 3D Scene Viewer lets you create dynamic visualizations, making it ideal for urban planning and environmental assessments.
SketchUp
SketchUp is user-friendly software perfect for creating detailed 3D models. It’s widely used in architecture and offers a vast library of models and plugins to enhance your mapping projects.
QGIS with 3D Plugins
QGIS provides an open-source alternative with excellent 3D modeling capabilities. The QGIS 3D Viewer and additional plugins let you visualize and analyze geospatial data effectively.
View Realist stereo slides in immersive 3-D with this affordable Radex viewer. Its lightweight design and simple operation make it perfect for enjoying vintage slides.
Blender
Blender is a versatile modeling tool that’s great for high-quality visualizations. With the right add-ons, it can handle GIS data for stunning 3D maps while offering extensive customization options.
CesiumJS
CesiumJS is a robust JavaScript library for creating 3D globes and maps in web applications. It can visualize large datasets and incorporates real-time data, making it perfect for interactive map projects.
When choosing software, consider your specific mapping needs, ease of use, and compatibility with the data sources you plan to use. Addressing these factors will enhance your 3D mapping efficiency and output quality.
Selection Criteria for Best Software
When choosing the right software for 3D map modeling, it’s essential to evaluate several critical factors to ensure your needs are met effectively. Consider the following criteria:
User-Friendliness
You need software that’s intuitive and easy to navigate. Programs like OcuMap excel with their user-friendly interface, allowing quick uploads and visualizations of 3D data. SketchUp offers a drag-and-drop feature that caters to both beginners and experienced users, making architectural and interior design modeling straightforward. Conversely, Blender boasts powerful tools but has a steeper learning curve, which may not suit everyone.
Feature Set
You should prioritize software with robust features tailored for your mapping projects. OcuMap provides unique capabilities like direct feature extraction from GPS images and videos, along with seamless GPS integration. Software such as ArcGIS Pro offers advanced analysis capabilities and rich visualization tools, while Blender supports high-quality visual outputs for detailed presentations.
Compatibility
You need to ensure that the software you choose is compatible with various data sources and formats. For example, QGIS provides open-source accessibility with extensive plugin options, making it ideal for a diverse range of geospatial data. CesiumJS specializes in interactive web-based maps, supporting various 3D data formats, while ensuring adaptability across different platforms.
Pricing Options
You must consider the cost of the software in relation to your budget and the features it offers. Some options like QGIS are completely free and open-source, while others such as ArcGIS Pro and SketchUp have licensing fees that can vary based on the package. Evaluate monthly versus one-time payment plans to find the best financial fit for your mapping needs.
Top 5 Best Software for 3D Map Modeling
Creating accurate and visually appealing 3D maps can be a challenge. With the right software, however, you can turn complex geospatial data into engaging visualizations. Here are the top five software options to consider for 3D map modeling.
1. Blender
Blender’s an open-source powerhouse that supports all aspects of 3D creation. It’s free and offers capabilities for modeling, animation, and rendering. Its community-driven resources make it accessible despite a steeper learning curve. You can use Blender for terrain modeling, visual effects, and even interactive simulations. Its flexibility allows you to tailor your workflow based on project needs, making it a vital tool for both beginners and seasoned professionals.
2. ArcGIS Pro
You may find that creating effective maps poses numerous challenges—balancing accuracy, aesthetics, and functionality. Advancements in technology and shifts in data accessibility have revolutionized mapping practices, but these changes also bring complexities. It’s vital to remain agile as you adapt to evolving data sources and visualization techniques.
Establishing Technical Context
Digital mapping relies heavily on Geographic Information Systems (GIS), which integrate hardware, software, and data to capture, manage, analyze, and visualize geographical information. Familiarizing yourself with GIS principles and tools is essential in overcoming mapping challenges and enhancing your output.
Key Methods to Improve Your Mapping Craft
- Utilize GIS Software: Tools like ArcGIS and QGIS excel at spatial analysis. ArcGIS provides advanced capabilities for data manipulation, while QGIS offers a versatile, open-source alternative.
- Leverage Data Sources: Access reliable datasets from sources like the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) or OpenStreetMap. These can enhance the accuracy of your maps.
- Employ Visualization Techniques: Use thematic mapping, such as choropleth maps, to represent data variations effectively. Tools like Tableau integrate mapping with business analytics for improved insights.
Addressing Common Technical Issues
You may encounter common pitfalls such as data misalignment, resolution issues, and poorly defined cartographic projections. Ensure you verify your data’s coordinate system and projection settings. Properly aligning your data layers not only improves spatial accuracy but also enhances the end user’s experience.
Exploring Data Visualization Options
- Interactive Maps: Tools like Mapbox or Leaflet allow for user engagement with your content through interactive, web-based maps.
- 3D Models: Use software like ArcGIS Pro for 3D visualizations, enabling users to gain a deeper understanding of spatial relationships.
- Dashboards: Combine multiple data layers and visual elements in a dashboard format using Microsoft Power BI or Google Data Studio, helping convey complex information clearly.
Providing Workflow Frameworks
Establishing an efficient workflow is critical for quality output. Consider the following framework:
- Data Collection: Gather data from reliable sources.
- Data Processing: Clean and preprocess your data in software like Excel or R.
- Mapping: Create maps using your chosen GIS software.
- Review: Implement peer reviews and QA/QC processes to ensure accuracy.
- Visualization: Enhance your maps with data visualization techniques.
Quality Control Tips
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic audits of your datasets to ensure they remain accurate and current.
- Seek Feedback: Collaborate with peers for input on your mapping projects, enhancing quality through multiple perspectives.
- Stay Updated: Keep your skills sharp by following industry standards and advancements in mapping technology. Familiarizing yourself with emerging trends ensures you maintain a competitive edge.
3. SketchUp
When tackling the challenge of creating engaging and precise 3D maps, SketchUp stands out as a premier tool. Its combination of ease of use and powerful features makes it suitable for a variety of mapping applications.
Key Features
- User-Friendly Interface: SketchUp’s intuitive design allows you to effortlessly create complex 3D structures through simple push and pull techniques. It’s built for both novices and seasoned users alike.
- 3D and Extension Warehouse: Access a vast library of free 3D models and plugins, which can expedite your modeling process and enhance your projects.
- File Compatibility: Export designs in formats like COLLADA (DAE) and OBJ, ensuring seamless integration with software like AutoCAD and Revit.
Ideal Use Cases
SketchUp is best suited for urban planning, architectural design, and landscape modeling. Its vast model library can save you time when designing urban environments. Additionally, educators in geography and environmental science can utilize SketchUp to create interactive learning experiences that visualize spatial data effectively. Whether you’re mapping a city block or designing a park, SketchUp’s versatility enhances both creativity and efficiency.
4. QGIS
QGIS is a highly adaptable mapping tool that’s particularly appealing for those seeking a free, open-source solution for 3D map modeling. It provides a solid foundation for generating insightful geospatial visualizations.
Key Features
- Data Upload and Integration: QGIS supports the upload of multiple geospatial data types, including Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), hillshades, and contour data, enabling comprehensive map creation.
- 3D Map View Generation: You can create a new 3D map view with just one click using the “New 3D Map View” option, efficiently visualizing your data in three dimensions.
- 3D Configuration: QGIS allows you to adjust vertical scales, exaggerating or minimizing elevation features, thus enhancing the overall clarity and usability of your map.
- Urban Planning: QGIS effectively visualizes complex terrain and infrastructure data, making it suitable for urban development projects.
- Environmental Science: Use QGIS to analyze and display ecosystem changes, land use, or habitat modeling with immersive 3D views.
- Educational Purposes: QGIS provides students and educators an accessible platform for learning geospatial concepts and for hands-on mapping projects in various disciplines.
With your mapping objectives in mind, QGIS stands out as a robust choice for those looking to harness 3D visualization efficiently.
5. Autodesk Maya
Learn Maya 2025 quickly with this guide, designed to teach you the fundamentals of 3D modeling, animation, and visual effects. Master essential tools and workflows through clear, step-by-step instructions.
Autodesk Maya stands out as a powerful software solution for 3D map modeling, combining robust features and exceptional versatility to meet various mapping challenges.
Key Features
- Comprehensive Modeling Tools: Maya provides extensive modeling techniques like Polygonal Modeling, NURBS Modeling, UV Mapping, and Sculpting. These tools help you create intricate 3D representations of geographical features, structures, or landscapes.
- Rigging and Animation: You can utilize Maya’s sophisticated rigging tools to build hierarchical structures. This functionality supports complex animations, essential for dynamic presentations of geographic data.
- Physics Simulations: With tools such as Bifrost, Maya allows you to simulate environmental effects, including smoke, fire, and snow, which can enhance the realism of your 3D maps.
- Urban Planning: In urban design, you can visualize various development scenarios using Maya’s modeling capabilities, allowing stakeholders to interact with potential projects effectively.
- Environmental Visualization: Maya excels in creating lifelike representations of natural landscapes, aiding in environmental assessments or educational purposes.
- Gaming Development: You can leverage Maya’s animation and simulation features to craft immersive virtual worlds, providing a realistic landscape experience for players.
- Architectural Visualization: By incorporating detailed models and animations, you can present architectural projects in a visually appealing manner, making it easier for clients to understand design concepts.
Comparison of Best Software for 3D Map Modeling
When selecting the right software for 3D map modeling, you’ll want to evaluate several critical factors: performance, supported file formats, and community support.
Performance
In terms of performance, efficient software can significantly influence your mapping outcomes. Pix4D Mapper offers impressive sub-centimeter accuracy in 3D modeling, although it may process smaller datasets slower. Simactive’s Correlator3D excels in speed and accuracy, thanks to its GPU processing capabilities, making it ideal for large datasets. Agisoft Metashape, another GPU-optimized option, matches these capabilities closely, providing rapid processing times, especially evident in benchmarking studies like those involving the Trinity Park dataset.
Supported File Formats
Software flexibility is crucial for smooth workflows. ArcGIS Pro supports a wide range of file formats, allowing you to import various datasets easily. QGIS, being open-source, excels in format compatibility, enhancing its appeal for diverse geospatial data types. SketchUp provides extensive integration with multiple file formats, ensuring seamless collaboration with other tools, which is vital for effective project execution.
Community Support
Strong community support is an asset that enhances your mapping experience. Software like Blender boasts a vast, active community that shares a wealth of tutorials and resources, easing the learning curve for users. QGIS benefits from an extensive network of users and contributors, offering forums and documentation to assist you in problem-solving. Pix4D Mapper has an established support community as well, while SketchUp’s user-friendly interface attracts a broad audience, resulting in numerous user-generated resources and plugins.
Conclusion
Choosing the right software for 3D map modeling can significantly impact your project’s success. By evaluating your specific needs and considering factors like user-friendliness and compatibility, you can find a tool that enhances your mapping efficiency. Whether you opt for the advanced features of ArcGIS Pro or the versatility of Blender, each software has unique strengths tailored to various applications.
Stay informed about industry advancements and community resources to make the most of your chosen software. With the right tools at your disposal, you’ll be well-equipped to create stunning and effective 3D maps that engage and inform your audience.