10 Best Field Tools for On-Site Map Data Collection That Improve Precision
Collecting accurate map data on-site is crucial for effective planning and decision-making. The right field tools can streamline your workflow and enhance data quality, making your projects more efficient. Explore the best options available to elevate your data collection game and ensure you’re equipped for success.
Best Field Tools for On-Site Map Data Collection
When you’re out in the field collecting map data, having the right tools is crucial for ensuring accuracy and efficiency. Here are some of the best field tools to enhance your data collection process:
GPS Devices
Navigate confidently with this GPS device featuring a bright 5" touchscreen and detailed North American maps. Stay informed with alerts for speed changes, school zones, and sharp curves, plus Tripadvisor ratings for points of interest.
GPS devices, such as the Garmin GPSMAP series, provide high-accuracy location tracking. Featuring features like waypoint management and 3D terrain mapping, these tools help in pinpointing exact locations.
Field Mapping Apps
Use field mapping applications like ArcGIS Field Maps or QField. These enable you to collect, edit, and manage geographic data right from your smartphone or tablet, allowing for real-time updates and efficient data capture.
Digital Tablets
Investing in ruggedized tablets, like the Microsoft Surface Go, ensures durability in rugged environments. It allows you to run mapping software while providing the flexibility to make annotations directly on your maps.
Drones
Drones equipped with aerial mapping software, such as DJI’s Phantom 4 RTK, offer a unique perspective for large areas. They produce high-resolution imagery and topographic maps with precision, making them invaluable for extensive surveys.
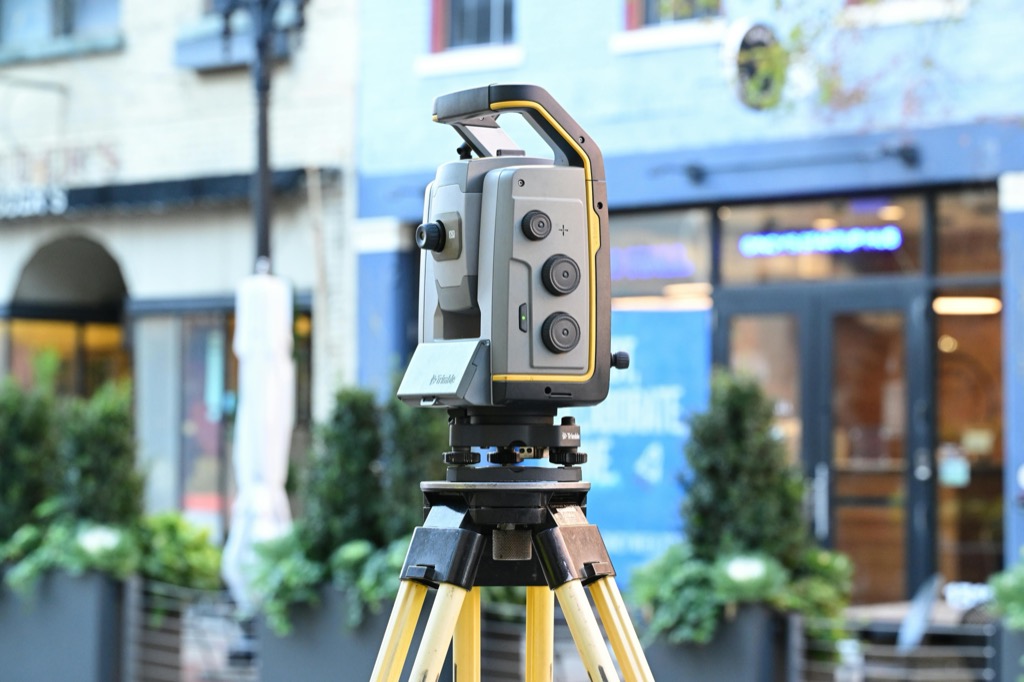
Total Station
A total station, like the Leica TS16, combines electronic theodolite functions with an electronic distance meter (EDM). It delivers precise angle and distance measurements, useful in boundary surveys and construction projects.
Protect your screen with AirGlass, a thin and light protector that maintains touchscreen sensitivity. Enjoy a clear, sharp view of your screen's content.
Laser Scanners
Tools, such as the Faro Focus, capture 3D data in high detail. They are perfect for creating detailed models of structures or landscapes, ensuring comprehensive data collection for advanced mapping.
Handheld Data Collectors
Devices like the Trimble Geo 7X are designed for rugged environments. These handheld units offer GPS capabilities and can withstand harsh conditions, making them ideal for remote data collection.
Power your Trimble GeoExplorer with this 15V adapter. It offers worldwide voltage compatibility and built-in surge protection for safe, reliable charging.
By utilizing these tools, you can enhance your mapping workflow, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of your on-site data collection efforts.
Digital Tools for Accurate Data Collection
Accurate map data collection starts with the right digital tools. These solutions enhance data quality and streamline your workflow in the field.
GPS Devices for Precision Mapping
Using high-quality GPS devices is essential for precise mapping. Look for devices that offer sub-meter accuracy, as this ensures your data points are reliable. Trimble R10 and Leica GS18 are excellent examples that combine strong GNSS capabilities with real-time correction. These devices not only improve accuracy but also support various mapping applications, helping you achieve high-resolution geospatial data in diverse environments.
Mobile Applications for Field Surveys
Mobile applications can significantly bolster your field surveys. Applications like ArcGIS Field Maps and Survey123 allow you to collect data on the go with customizable forms and real-time syncing capabilities. These tools feature offline functionality, ensuring you can continue working in remote areas. Incorporating mobile apps also enhances collaboration, as you can instantly share data with your team, reducing errors and improving overall project efficiency.
Manual Tools for Effective Data Gathering
Using manual tools can significantly enhance your precision during on-site data collection. These tools complement digital methods and help you gather accurate data efficiently.
Measuring Tapes for Distance Accuracy
Measuring tapes are indispensable for precise distance measurements in the field. They’re cost-effective and straightforward to use, making them ideal for smaller distances. When measuring, ensure you choose a tape with clear markers and a sturdy design. Using a 100-foot or 50-meter tape can cater to various projects, allowing you to avoid potential errors that can arise with longer measurements. With measuring tapes, you can confidently capture distances, ensuring the accuracy of your map data.
Compasses for Orientation and Navigation
Compasses are vital for accurate orientation and navigation in field mapping. These tools help you determine direction relative to magnetic north. Remember to account for magnetic declination, which can affect your readings. For example, using a compass with an adjustable declination feature lets you adjust for local geomagnetic differences. Incorporating a good-quality compass improves your navigation strategy and ensures that you maintain the correct path while collecting data in complex terrains.
Drones for Aerial Data Acquisition
Drones have revolutionized the way you can collect geographic data, providing unique advantages in mapmaking and data analysis. By utilizing aerial imagery, you can capture high-resolution data that enhances the quality of your maps.
UAV Technology for High-Resolution Imaging
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras or multispectral sensors enable you to obtain detailed images with accuracy. The DJI Phantom 4 RTK, for instance, leverages Real-Time Kinematics (RTK) for precise georeferencing, producing centimeter-level accuracy. By integrating this technology within your workflows, you can effortlessly collect extensive data sets over large areas, streamlining your mapping projects.
Benefits of Using Drones in Mapping
Utilizing drones in mapping provides several advantages, including:
- Cost Efficiency: Drones reduce the need for manned aerial surveys, lowering overall project costs.
- Access to Inaccessible Areas: Drones can reach remote locations where traditional surveying methods may struggle, such as rugged terrains or densely forested areas.
- Rapid Data Collection: You can transfer data quickly, allowing for faster analysis and project turnaround.
- High-Quality Imagery: Drones capture images at various resolutions, enhancing the detail and utility of your maps.
By incorporating drone technology into your mapping toolkit, you improve both the efficiency and quality of your data collection efforts.
Field Notebooks for Field Data Recording
Field notebooks are essential tools for documenting observations and metadata crucial for map accuracy. You can streamline your data collection efforts with a well-organized notebook, capturing detailed information directly in the field.
Importance of Keeping a Detailed Log
Keeping a detailed log ensures you have accurate data for future analysis. Documenting your observations, measurements, and contextual information can help clarify decisions made during the mapping process. Frequent entries allow you to track changes over time, supporting quality assurance. For example, noting weather conditions or site access issues can significantly impact the interpretation of the data later on.
Tips for Organizing Field Notes Efficiently
Organize your field notes using a consistent structure to enhance usability.
- Use numbered pages to easily reference important entries.
- Create sections for different data types, like observations, measurements, and sketches.
- Utilize symbols or shorthand for quick note-taking, while ensuring you maintain clarity.
- Color-code entries to categorize data by importance or urgency.
- Incorporate diagrams or sketches to illustrate complex features relevant to your mapping.
By implementing these strategies, you’ll enhance the clarity and functionality of your field notebooks, ultimately leading to more effective data collection.
Data Management Tools for Analysis
Effective data management is crucial for turning raw map data into meaningful insights. Utilizing the right tools and practices can enhance your analysis and ensure that your findings are reliable and actionable.
Software for Analyzing Collected Data
You should consider dedicated software solutions for data analysis. Tools like ArcGIS Pro and QGIS offer powerful capabilities for statistical analysis and spatial data manipulation. These platforms enable you to visualize patterns, run geoprocessing tasks, and create detailed maps that elucidate your findings. Integrating R or Python with GIS software can further enhance your analytical capabilities, allowing for custom scripts that automate repetitive tasks or perform complex calculations.
Master ArcGIS Pro 3.2 with this comprehensive guide. Learn essential GIS workflows and data management techniques for effective spatial analysis.
Best Practices for Data Storage and Backup
You must prioritize data storage and backup to safeguard your collected map data. Utilize cloud-based solutions like Google Drive or Dropbox for automatic syncing and easy access across devices. Implement local backup strategies using external hard drives or Network Attached Storage (NAS) systems to create redundant copies. Ensure you maintain organized file structures, labeling datasets clearly with version control practices to track changes and prevent data loss during analysis. Regular backups minimize the risk of losing critical data due to hardware failures or accidental deletions.
This durable steel mailbox protects your mail with a secure, customizable 3-digit combination lock. Its large capacity holds multiple letters and newspapers, while the transparent cover lets you easily check for new mail.
Access your files securely from anywhere with Google Drive. Back up your photos, videos, and more with reliable cloud storage.
Conclusion
Choosing the right field tools for on-site map data collection can significantly impact your project’s success. By leveraging a mix of digital and manual tools you can enhance accuracy and efficiency in your data gathering efforts. Whether you opt for high-accuracy GPS devices drones or rugged tablets each tool plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality of your map data.
Remember to document your observations meticulously and manage your data effectively. This comprehensive approach not only improves collaboration but also sets the stage for informed decision-making. As you explore these tools keep in mind that investing in the right technology will pay off in the long run by streamlining your workflow and enhancing the reliability of your results.