10 Best Portable Mapping Devices for Field Work That Improve Precision
In the fast-paced world of fieldwork, having the right tools can make all the difference. Portable mapping devices have revolutionized how professionals navigate and collect data in remote locations. Discovering the best options for your needs can enhance efficiency and accuracy, ensuring you stay ahead in your projects.
Best Portable Mapping Devices For Field Work
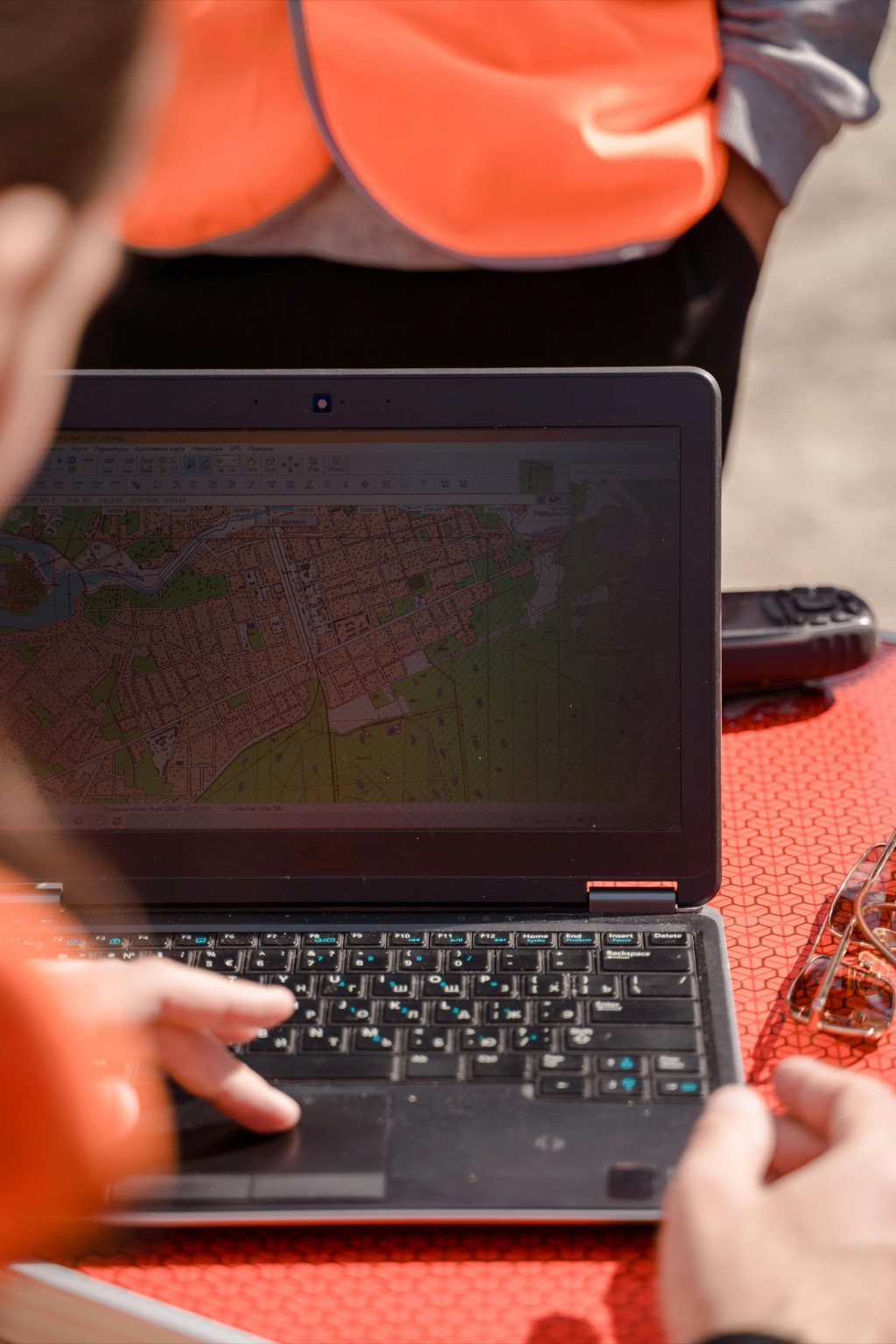
Understanding your mapping challenges is the first step in selecting an effective portable mapping device. In fieldwork, accuracy, durability, and ease of use are critical, especially in remote areas.
1. Garmin Oregon 750t
Navigate any adventure with this rugged, IPX7 water-resistant GPS device featuring a sunlight-readable touchscreen. Its built-in ABC sensors (altimeter, barometer, compass) and customizable activity profiles ensure accurate tracking for hiking, biking, and more.
It’s a versatile handheld GPS unit that combines high-sensitivity GPS with outdoor navigation features. You can add topographic maps, and it’s rugged enough for any environment.
2. Trimble Geo 7X
Power your Trimble GeoExplorer with this 15V adapter. It offers worldwide voltage compatibility and built-in surge protection for safe, reliable charging.
It’s ideal for professionals needing high-accuracy data collection. With GNSS support and field-ready design, you can gather precise geospatial data with ease, even in tough conditions.
3. Bad Elf GNSS Surveyor
It’s a compact, Bluetooth-enabled tool that connects to tablets and smartphones. You can utilize it for real-time differential GNSS accuracy, enhancing your mapping operations.
4. Leica Zeno 20
Experience exceptional clarity and touch sensitivity with the AirGlass screen protector. Its ultra-thin design provides reliable scratch protection without compromising your device's display quality.
It combines a user-friendly interface with precise measurements. The device’s versatility makes it suitable for various surveying tasks, with options for integrating various GIS formats.
5. Android Tablets with GIS Software
Master ArcGIS Pro 3.2 with this comprehensive guide. Learn essential GIS workflows and data management techniques for effective spatial analysis.
Using devices like Samsung Galaxy Tab Active3 lets you leverage GIS applications in a portable format. You can use software like ArcGIS Collector or QField to manage your maps in the field.
The Galaxy Tab Active5 is a rugged, water-resistant tablet built for demanding work environments. Its long-lasting, replaceable battery and glove-friendly touchscreen ensure productivity in any situation.
By choosing one of these devices, you ensure a more efficient and accurate fieldwork process, crucial for high-quality mapping results.
Top Features To Consider
When selecting portable mapping devices for fieldwork, you need to evaluate several essential features to ensure optimal performance and usability in various terrains.
Battery Life
Battery life is crucial for extended usage in the field. Look for devices with robust batteries, like the Te-Rich Handheld GPS GNSS Receiver, which offers an impressive 32 hours. The SMAJAYU R26 GNSS Surveying System also provides up to 14 hours of continuous use, ideal for large surveying projects. Always consider how long you’ll spend in the field without a power source.
GPS Accuracy
GPS accuracy directly impacts your mapping results. Devices like the Garmin GPSMAP 67i are recognized for their precise location tracking, essential in professional surveying. Ensure the GPS system can maintain high accuracy even in challenging environments, such as dense forests or urban areas. Review specifications for accuracy ratings, typically stated in meters.
Display Quality
Display quality can influence your ability to read data effectively during fieldwork. Look for devices with high-resolution screens that are sunlight-readable, such as the Leica Zeno 20, which provides excellent visibility in bright conditions. A responsive touch interface can also enhance usability, making it easier to zoom in and out or switch between functions efficiently.
Durability
Durability ensures your device withstands various environmental challenges. Choose rugged models that meet industry standards for water and dust resistance, like the Bad Elf GNSS Surveyor. Ensure the device has passed drop tests, allowing it to endure rough handling in the field. A sturdy design can make the difference when operating in harsh conditions, ensuring your equipment lasts longer.
Best Portable Mapping Devices Reviewed
Explore top portable mapping devices that excel in fieldwork. These tools enhance navigation and data collection, making them essential for professionals.
Device 1: Garmin GPSMAP 66i
The Garmin GPSMAP 66i stands out with its robust feature set and reliability. It’s equipped with InReach technology, offering satellite messaging in remote areas. The device features a bright, clear screen and highly customizable settings, allowing you to tailor notifications if you stray from your route. Plus, it supports multi-GNSS systems like GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo, ensuring accurate navigation across varied terrains.
Device 2: Trimble Juno T41
The Trimble Juno T41 is known for high accuracy and durability, perfect for demanding fieldwork conditions. Its rugged design withstands harsh environments while providing reliable spatial data collection. With Trimble’s advanced GNSS technology, it offers precision location tracking, benefiting surveyors and outdoor professionals alike. The device’s intuitive interface makes data entry easy, enhancing productivity during field tasks.
Device 3: Bad Elf GNSS Pro
The Bad Elf GNSS Pro delivers exceptional accuracy and versatility for mapping professionals. This device integrates seamlessly with GIS apps on mobile platforms, providing real-time positioning data. It boasts a high battery life, allowing for extended field use without frequent charging. Additionally, it supports various coordinate systems, enabling you to work globally while maintaining precision in your projects.
Device 4: Magellan eXplorist 310
The Magellan eXplorist 310 is tailored for both recreational mapping and professional uses. It offers a user-friendly interface, making it accessible for newcomers and experts. With detailed topographic maps pre-loaded, you can navigate effortlessly through diverse landscapes. Its rugged construction ensures durability in tough conditions, while its long-lasting battery supports sustained operation during lengthy fieldwork sessions.
Mapping Challenges and Technical Context
Comparison Of Pricing
Mapping often presents several challenges, particularly when you’re in remote locations or dealing with dynamic environments. For instance, you may encounter inconsistent data sources, environmental interference, or the need for real-time positioning accuracy. Understanding the technical requirements of your mapping tasks can help you select the right tools.
Consider the Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) as the foundation of modern mapping technology. These systems provide enhanced accuracy, but their effectiveness depends on various factors, including satellite visibility and environmental conditions. You should familiarize yourself with the types of GNSS available, such as GPS and GLONASS, to ensure reliable positioning.
Key Methods and Examples
To effectively tackle mapping tasks, here are key methods you can implement:
- Use Differential GNSS (DGNSS): This method improves accuracy by using a network of fixed ground stations. For example, the Trimble Geo 7X offers DGNSS capability, allowing for centimeter-level accuracy.
- Integrate GIS Software: Utilize GIS applications to manage and visualize your data effectively. Tools like ArcGIS and QGIS provide powerful functionality for analysis and representation.
- Employ Mobile Mapping Devices: Devices such as the Bad Elf GNSS Surveyor can be integrated with smartphones or tablets, giving you the flexibility to collect and analyze data on-site.
Common Technical Issues
When mapping in the field, you might encounter various technical challenges:
- Signal Loss: This is often due to surrounding terrain or dense foliage. Select a device with robust signal acquisition features, like the Garmin GPSMAP 66i, known for its strong reception capabilities.
- Data Inconsistency: Inaccurate location readings can arise from poor satellite coverage. Ensure you’re familiar with your device’s error margins and use correction services where possible.
- Battery Life limitations: Long fieldwork days can drain batteries quickly. Opt for devices with extended battery life, like the Te-Rich Handheld GPS GNSS Receiver, which lasts up to 32 hours.
Data Visualization Options
Visualizing data effectively is essential for interpreting your mapping results. Consider the following approaches:
- Layering Information: Use thematic layers to differentiate types of data, such as elevation or land use. This can enhance readability and aid in analysis.
- Interactive Maps: Tools like Mapbox allow you to create interactive visualizations that engage your audience, making data exploration more intuitive.
- Graphical Representation: Utilize charts or infographics to present complex information succinctly. This can improve stakeholder understanding and decision-making.
Workflow Frameworks
A streamlined workflow can significantly enhance your mapping efficiency. Here’s a framework to consider:
- Planning Phase: Begin by defining objectives and data requirements for your mapping project.
- Data Collection: Use suitable tools for high-accuracy data gathering. Devices like the Leica Zeno 20 are ideal for professional surveys.
- Data Processing: Analyze and refine data using GIS software, ensuring quality control measures are in place.
- Visualization and Reporting: Convert your findings into clear, comprehensible maps or reports for your intended audience.
Quality Control Tips
Maintaining high standards of quality in your mapping projects is critical. Here are some tips:
- Regular Calibration: Always calibrate your instruments and verify data accuracy regularly, especially before fieldwork.
- Cross-Validation: Compare collected data with existing datasets to check for inconsistencies or errors.
- Documentation: Keep meticulous records of your methodologies, data sources, and technical limitations to inform future projects.
By understanding these elements, you can improve your mapping practices, making your data collection and visualization efforts more effective and reliable.
User Reviews And Experiences
User reviews and experiences provide valuable insights into the practical use of portable mapping devices. Professionals and casual users alike share their feedback, helping you make informed decisions.
Professional User Feedback
Professionals often praise the SMAJAYU GNSS Surveying System for its remarkable centimeter-level accuracy and adaptability in tough environments. Users highlight features such as Bluetooth connectivity and multi-module support that enhance its versatility for large-scale surveying projects. Similarly, the Garmin GPSMAP 67i stands out for its rugged design and robust multi-GNSS functionality, receiving accolades for reliable performance in remote locations.
Casual User Feedback
Casual users appreciate the Te-Rich Handheld GPS GNSS Receiver for its lightweight design, making it easy to carry during outdoor activities. Its impressive 32-hour battery life is often noted as a significant advantage in the field. Users also commend the intuitive interface and practicality for hiking and recreational mapping, showcasing its usability in everyday situations.
Conclusion
Choosing the right portable mapping device can significantly enhance your fieldwork experience. With the right tools in hand you’ll navigate remote areas with confidence and collect data more efficiently. Each device discussed offers unique advantages tailored to various needs whether you prioritize accuracy durability or battery life.
By understanding the specific challenges you face in mapping you can make informed decisions that elevate your projects. Remember to consider user experiences and reviews as they provide valuable insights into real-world performance. Equip yourself with the best portable mapping technology and watch your fieldwork transform into a more streamlined and productive endeavor.