10 Best GIS Plugins for Advanced Spatial Analysis That Unlock Insights
In today’s data-driven world, mastering spatial analysis is crucial for making informed decisions. GIS plugins can supercharge your capabilities, offering tools that enhance data visualization and analysis. Discover the best GIS plugins that elevate your spatial analysis game and unlock new insights.
Best GIS Plugins For Advanced Spatial Analysis
You face numerous mapping challenges when it comes to advanced spatial analysis, but leveraging the right GIS plugins can significantly boost your efficiency and accuracy. These tools enhance data manipulation, analysis, and visualization.
QGIS Processing Plugin
Master QGIS with this hands-on guide. Learn advanced techniques through practical, step-by-step examples to unlock the software's full potential.
QGIS offers a Processing framework to execute complex spatial analysis tasks. It integrates various algorithms for vector and raster data, allowing custom workflows.
Spatial Analyst Extension for ArcGIS
This extension provides advanced raster analysis capabilities. You can perform functions like surface analysis, distance analysis, and statistical analysis with ease.
GRASS GIS
Master geospatial analysis with GRASS GIS using this comprehensive guide. Learn practical techniques for managing, processing, and visualizing geographic data effectively.
GRASS GIS integrates seamlessly into your workflows, enabling robust geostatistical and raster modeling. Utilize it for terrain analysis and hydrological modeling.
SAGA GIS
SAGA aligns with QGIS and offers a range of specialized modules for digital elevation and geostatistical analyses. Its capability in terrain analysis can enhance your projects significantly.
Addressing Technical Issues
Use documentation and community forums to troubleshoot plugin problems you might encounter. This ensures you take full advantage of each tool’s functionalities.
Data Visualization Options
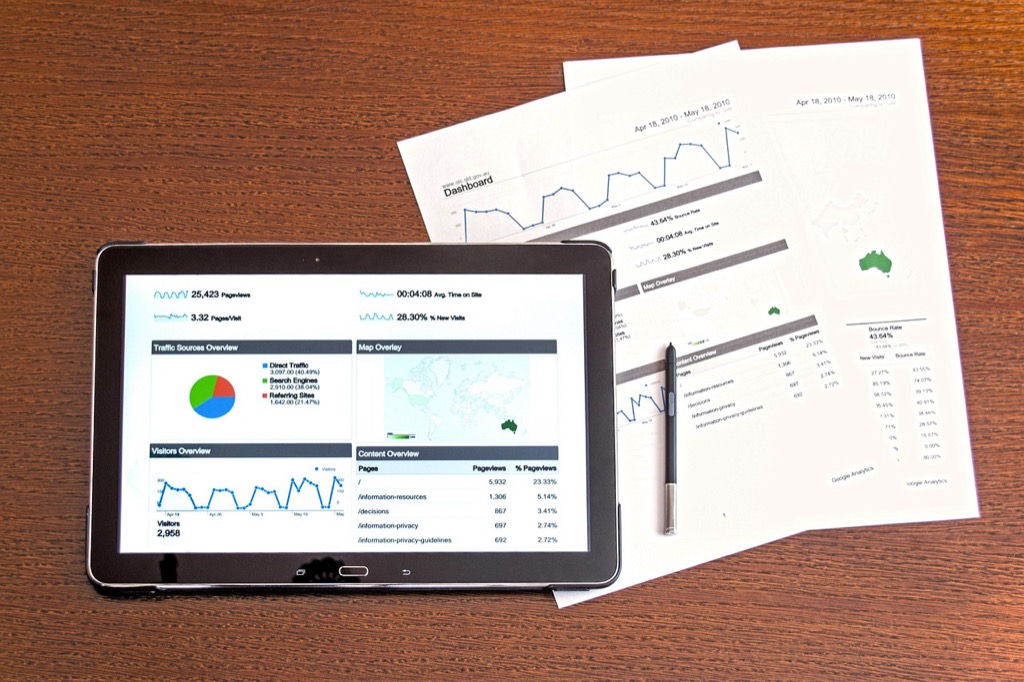
Incorporate data visualizations that represent complex spatial relationships effectively. Plugins like “Data Plotly” for QGIS allow you to create interactive plots right within your GIS environment.
Build interactive dashboards and data apps effortlessly with Plotly and Dash. Leverage a complete Python web framework, eliminating the need for JavaScript.
Workflow Frameworks
Develop a structured workflow by combining these plugins with your existing GIS software. Start with data acquisition, move to analysis using the plugins, and end with visualization and dissemination of results.
Master ArcGIS Pro 3.2 with this comprehensive guide. Learn essential GIS workflows and data management techniques for effective spatial analysis.
Quality Control Tips
Always validate results by cross-referencing with reliable data sources. Implementing a Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC) procedure ensures the integrity of your spatial analysis outputs.
By embracing these methodologies and tools, you’ll enhance your mapping capabilities and deliver more insightful analyses.
Analyzing Spatial Data With Plugins
Navigating the complexities of spatial data analysis can be challenging. Utilizing GIS plugins significantly enhances your mapping capabilities, allowing for improved data handling and visualization.
Understanding GIS Plugins
GIS plugins are essential tools that expand the functionality of your GIS software. They integrate seamlessly with your existing platforms, allowing you to perform a wider range of analyses and visualizations. Tools like the QGIS Processing Toolbox or the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst Extension provide advanced capabilities, from spatial statistics to custom geoprocessing tools. By incorporating these plugins, you can tailor your mapping experience to fit specific analytical needs.
Used book in good condition, ready to be enjoyed. Expect possible minor wear.
Become proficient in spatial data analysis with QGIS 3.x using this in-depth guide. Learn to leverage Python with QGIS 3.4 and 3.6 for geospatial development.
Importance of Spatial Analysis in GIS
Spatial analysis plays a crucial role in extracting meaningful insights from spatial data. By analyzing geographic relationships, patterns, and trends, you can make data-driven decisions. For instance, using plugins like SAGA GIS or GRASS GIS, you can conduct complex terrain analyses or hydrological modeling, essential for environmental studies. Emphasizing efficiency and accuracy, spatial analysis enhances your ability to visualize data effectively and make informed choices based on comprehensive evidence.
Top 10 Best GIS Plugins For Advanced Spatial Analysis
You face challenges every day as a cartographer, from managing large datasets to ensuring the accuracy of your spatial analyses. Incorporating quality GIS plugins can significantly enhance your workflow, allowing you to perform advanced spatial analyses with ease and precision. Here are ten essential GIS plugins that can elevate your mapping capabilities:
1. QGIS Processing Toolbox
QGIS Processing Toolbox allows you to run extensive algorithms from various data processing providers like GDAL and GRASS. You can automate workflows and streamline complex tasks, making it ideal for advanced spatial analysis. Integrate it with your existing QGIS projects to unlock additional functionalities without switching platforms.
2. ArcGIS Spatial Analyst
ArcGIS Spatial Analyst is a powerful extension tailored for raster and vector data analysis. With tools to derive information, perform location suitability assessments, and calculate optimal routes, you can reveal important insights. Its ability to interpolate values and conduct distance analyses enhances your analytical capabilities significantly.
3. GRASS GIS
GRASS GIS is an open-source tool offering robust analytical capabilities, especially for environmental studies. Utilize its unique functions like raster geoprocessing and vector-based spatial modeling to handle complex operations efficiently. By integrating GRASS GIS into your workflows, you can achieve high precision in your spatial analyses.
4. SAGA GIS
SAGA GIS is renowned for its specialized geoscientific functionalities. Embrace its user-friendly interface to perform detailed terrain analyses and hydrological modeling. You can also extend its capabilities through scripting, making it a flexible tool for various spatial data applications.
5. GeoPandas
GeoPandas simplifies the process of working with geospatial data in Python. You can easily manage and analyze GIS data in your Python workflows, leveraging pandas for data manipulation. This integration enables you to create sophisticated analyses with minimal coding while enhancing data visualization options.
6. RGDAL
RGDAL is a crucial package for accessing spatial data in R. It acts as a bridge between R and various GIS formats, enabling easy import and export of spatial data. Using RGDAL, you can conduct advanced statistical analyses and create custom visualizations that can easily complement existing GIS workflows.
7. GDAL
GDAL (Geospatial Data Abstraction Library) is an essential library for reading and writing raster and vector geospatial formats. With GDAL, you can convert and manipulate different file types, streamlining data preparations for analyses. Its high-quality output makes it a reliable choice for GIS professionals.
8. PySAL
PySAL is a library designed for spatial data analysis in Python, emphasizing statistics. You can perform spatial econometric analyses, such as clustering and regression, to investigate relationships within your data. By integrating PySAL, you can combine statistical methods with your GIS applications effectively.
9. Map Algebra
Map Algebra is a workflow approach used in both raster and vector analyses. It allows you to perform operations on multiple layers simultaneously, simplifying complex calculations. You can integrate this technique in ArcGIS or QGIS projects to enhance your data visualization and statistical analyses.
10. PostGIS
PostGIS extends the functionality of PostgreSQL for spatial data storage and queries. Use it to develop efficient data models and perform advanced spatial queries on large datasets. By leveraging PostGIS, you gain the ability to handle complex geographic data while ensuring data integrity and performance.
These GIS plugins, grounded in industry standards and practical applications, will help you improve your mapping process. Remember to stay vigilant about data quality and consider how these tools can be integrated into your existing workflow while providing accurate results.
Features of Each Plugin
In the dynamic world of cartography, you often face challenges like effectively representing complex data and ensuring your maps communicate clearly. Understanding the intricacies of data visualization and the tools at your disposal can significantly enhance your mapping outcomes.
Technical Context of Cartography
Cartography merges art and science, demanding accuracy and aesthetic appeal. Familiarizing yourself with industry standards, such as the ISO 19115 for metadata, ensures that your maps maintain integrity and usability. You should leverage modern GIS software and mapping applications that facilitate data analysis, visualization, and accessibility.
Key Methods for Effective Mapping
- Utilize GIS Tools: Tools like QGIS or ArcGIS are essential for spatial analysis and visualization. These platforms allow you to manipulate geospatial data efficiently.
- Apply Thematic Mapping: Use color gradients and symbols to emphasize data patterns, aiding viewers in understanding distributions or trends.
- Incorporate Interactivity: Tools like Leaflet or Mapbox can help create interactive maps that engage users. This approach encourages exploration and enhances user experience.
Addressing Common Technical Issues
You’ve likely encountered issues such as data misalignment or projection errors. Here are some remedies:
- Data Alignment: Ensure datasets share the same coordinate system. Use tools in GIS platforms to reproject layers when necessary.
- Projection Errors: Choose appropriate projections for your map’s purpose. The Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) is often suitable for localized areas, while the Robinson projection may work better for world maps.
Exploring Data Visualization Options
Effective data visualization is crucial for successful cartography. Consider these options:
- Charts and Graphs: Integrate visual tools in your maps for clarity. Bar charts or pie charts can represent statistical data concisely.
- Heat Maps and Choropleth: These techniques visualize variations in datasets across geographical areas, making patterns easier to identify.
- Symbolization: Adjust colors, shapes, and sizes of symbols to convey information or importance effectively.
Workflow Frameworks for Efficient Mapping
A structured workflow can streamline your mapping projects:
- Data Collection: Identify relevant data sources—reliable databases, government statistics, or crowd-sourced information.
- Data Processing: Clean and format your data to ensure accuracy. Use tools like OpenRefine for this purpose.
- Map Design: Sketch preliminary designs to conceptualize layout and elements. Use prototyping tools if necessary.
- Map Review: Conduct internal reviews to catch errors or areas for improvement before publishing.
Quality Control Tips
Quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) are essential in mapping. Implement these practices:
- Peer Reviews: Involve colleagues to critique and suggest improvements on your maps.
- Cross-Checking Data: Verify data from multiple reputable sources before finalizing your maps.
- User Feedback: Collect insights from users post-publication to identify potential areas for enhancement in future mapping projects.
By mastering these techniques and tools, you’ll enhance your mapping capabilities, making your cartographic outputs more effective and user-friendly.
Comparing Performance and Usability
When enhancing your spatial analysis capabilities, understanding the performance and usability of GIS plugins is crucial. You’ll want to balance efficiency with user-friendly features to achieve optimal results.
Performance Metrics for GIS Plugins
For assessing performance, focus on tools that measure key metrics. Integrated tools like JMeter help you analyze system performance in ArcGIS by simulating user scenarios. You can identify bottlenecks and optimize response times, ensuring smoother operations. Using tools like PerfTools in ArcGIS Pro, you can measure map drawing speeds; however, keep in mind that it doesn’t provide layer-by-layer statistics due to the software’s rendering pipeline intricacies.
Usability Considerations for Users
Prioritizing usability enhances your mapping experience. Look for plugins with intuitive interfaces and robust documentation. QGIS Processing Toolbox, for example, offers streamlined workflows, enabling you to automate repetitive tasks effectively. Common plugins should facilitate easy data manipulation and visualization, which helps you produce maps that are not only functional but also visually appealing. Consider user feedback and community support when choosing plugins, as they can significantly improve your overall workflow and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Harnessing the power of GIS plugins can significantly elevate your spatial analysis capabilities. By integrating the right tools into your workflows, you can unlock new insights and streamline your data visualization processes. Whether you’re focused on environmental studies or urban planning, each plugin offers unique features that can cater to your specific needs.
Investing time in mastering these plugins not only enhances your analytical skills but also ensures your outputs are accurate and visually appealing. As you explore these tools, remember to validate your results and engage with the community for support. With the right approach, you can transform your spatial data into compelling narratives that drive informed decision-making.